Hi.
3) Armament: Machine Guns
IJA and IJN had several different MGs and machine cannons in their arsenals:
a) french 8 mm Hotchkiss MG

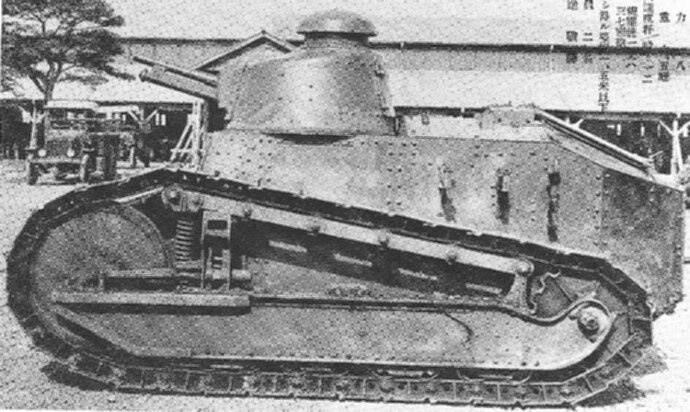
IJA used Hotchkiss-type MGs from 1904 on, rechambered to the domestic 6,5 mm X 50,5 mm Arisaka ammunition. With the Renault FT-17 tanks at least 6 original french 8 mm Hotchkiss MGs were bought in 1919 and several more with the Medium Mk A Whippets. These were standard french army issue Hotchkiss Modellé 1909. The main difference to the infantry version was the use of belted ammunition with 250 shots instead of 24 shot ammo strips.
It´s quite possible that these MGs were replaced by the rechambered japanese version.
Caliber: 8 mm X 50 mm rimmed Type Lebel (6,5 mm X 50,5 mm semi-rimmed Type Arisaka)
Length: 1310 mm
Barrel length: 770 mm
Grooves: 4
Weight: 23,7 kg
Rate of Fire theoretical: 600 shots/min
practical: up to 500 shots/min
Muzzle velocity: 710 m/sec
b) Vickers 7,7 mm MG:
In 1926 IJA bought 3 Vickers Mk C Medium Tanks, armed with these MGs. The water cooling was usefull but made the gun vulnerable to damages inflicted by bullets and splinters. Therefore this MGs were not used by IJA. The tanks were just tested and finally scrapped. IJN used this MG for boarding parties and armament of small ships.
Data:
Caliber: 7,7 X 56 mm rimmed
Length: 1100 mm
Barrel length: 720 mm
Grooves: 4
Weight: 13 kg
Maximum range: 4100 m
Effective range: 800 m
Rate of Fire theoretical: 600 shots/min
practical: 450 shots/min
Muzzle velocity: 740 m/sec
c) Type Taisho 3 6,5 mm MG

This weapon was a modification of the Type Meiji 38 Hotchkiss-type heavy MG made by Army Technical Bureau under command of NAMBU Kijiro from 1914 on. The Hotchkiss ejection mechanism was replaced by the Lewis-type ejection increasing firing speed and reliability. Other changes were done to increase barrel cooling and handling. The result was adopted officially in 1915.
For IJA tank troops the Hotchkiss-type MGs were replaced by this MG in the mid-1920th and all new tanks were armed with it.
Data:
Caliber: 6,5 X 50,5 mm semi-rimmed Type Arisaka
Length: 1204 mm
Barrel length: 742 mm
Grooves: 4
Weight: 27,9 kg
Maximum range: 2000 m
Effective range: 600 m
Rate of Fire theoretical: 600 shots/min
practical: 120 shots/min (continuos fire 480 shots/min)
Muzzle velocity: 740 m/sec
d) Type 91 6,5 mm Tank MG
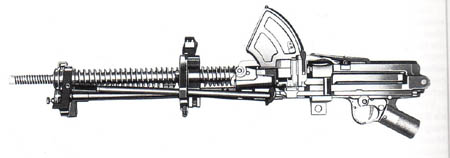
This MG was a modified version of the Type Taisho 11 6,5 mm lMG used by ground forces. It was air-cooled and hopper-fed with oiled 5-shot-clips. The ammunition was the standard Type Meiji 38 6,5 mm rifle ammunition but with reduced propellant charge. This was necessary to reduce failures due to ripped cartridges inside the chamber. It was introduced in 1931 as the designation indicates.
The forward telescope bracket was attached to the vehicle MG-port. The weapon was then fixed inside a quick-release mount.
In the mid-1930s a removable barrel armour was added to reduce damages by bullets and splinters. A bipod could be attached to use the MG outside the vehicle. If the crew had to bail out without immediate danger e. g. due to internal fire or enemy AT-weapons the MG should be taken with the gunners.
This weapon was used in allmost all IJN and IJA vehicles until it was replaced by its successor in the late 1930th.
Data:
Caliber: 6,5 X 50,5 mm semi-rimmed Type Arisaka
Length: 838 mm
Barrel length: 488 mm
Grooves: 4
Weight: 10,15 kg
Maximum range: 2000 m
Effective range: 600 m
Rate of Fire theoretical: 500 shots/min
practical: 80 - 120 shots/min
Muzzle velocity: 700 m/sec
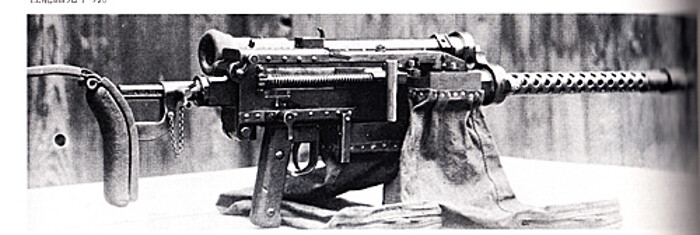
e) Type 97 7,7 mm Tank MG
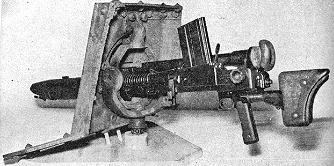
Successor of the Type 91 Tank MG. It was based on the czech MG ZB 26/ZB 30s captured in larger numbers during the 1935/1936 northern China operations. This weapons were tested and modified by Nambu Weapons Factory. Main modification was rechambering to the Type 92 MG ammunition developed for the Type 92 7,7 mm Heavy MG (the well known “Woodpecker”). The MG was fed by a box-type 20 shot magazine similar to the ZB-series instead of the 30 shot curved magazine used with the Type 96 6,5 mm lMG, a parallel Nambu development.
This MG was used in allmost all armoured vehicles until 1945 replacing the Type 91 Tank MGs.
Data:
Caliber: 7,7 X 56 mm semi-rimmed
Length: 1180 mm
Barrel length: 712 mm
Grooves: 4
Weight: 11,14 kg
Maximum range: 2000 m
Effective range: 600 m
Rate of Fire theoretical: 500 shots/min
practical: 80 - 120 shots/min
Muzzle velocity: 730 m/sec
g) Type 4 experimental 7,7 mm Machine gun
Late war development of a successor to the type 97 MG. There is not much known on this weapon as most data were destroyed at surrender. It is somewhat similar to the Ho-103 12,7 mm aircraft MG but chambered for the Type 99 7,7 mm round. The gun was belt fed from the left side.
no data found
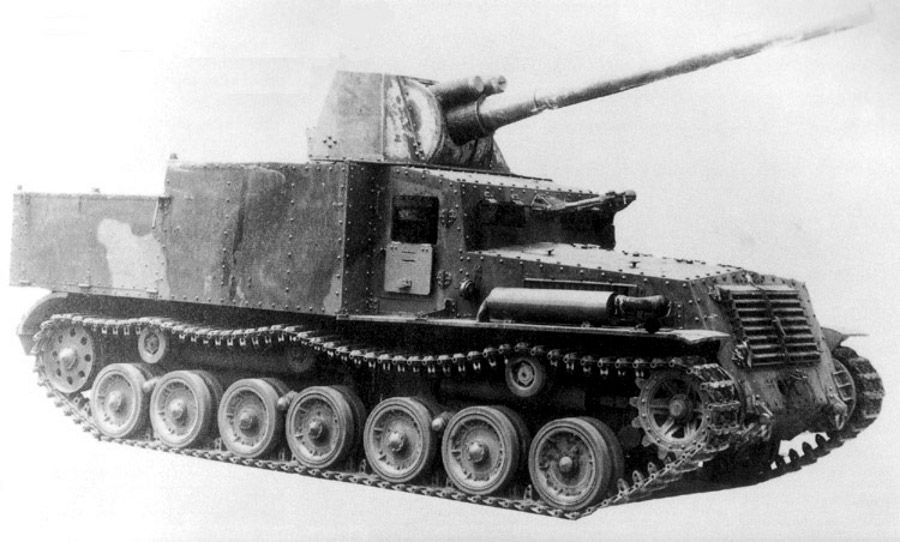
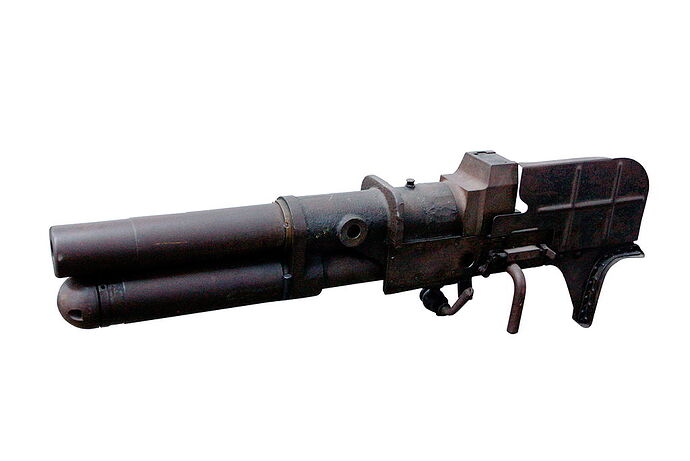
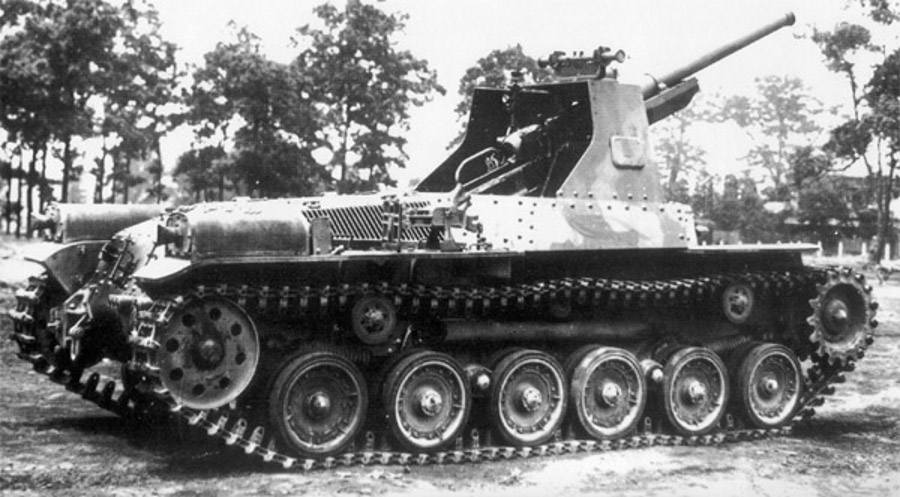
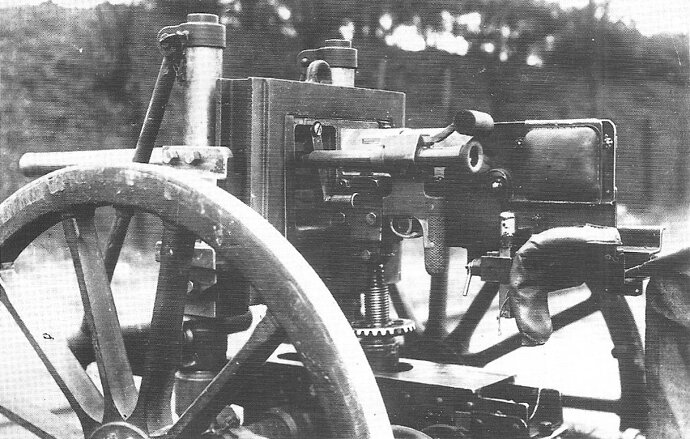
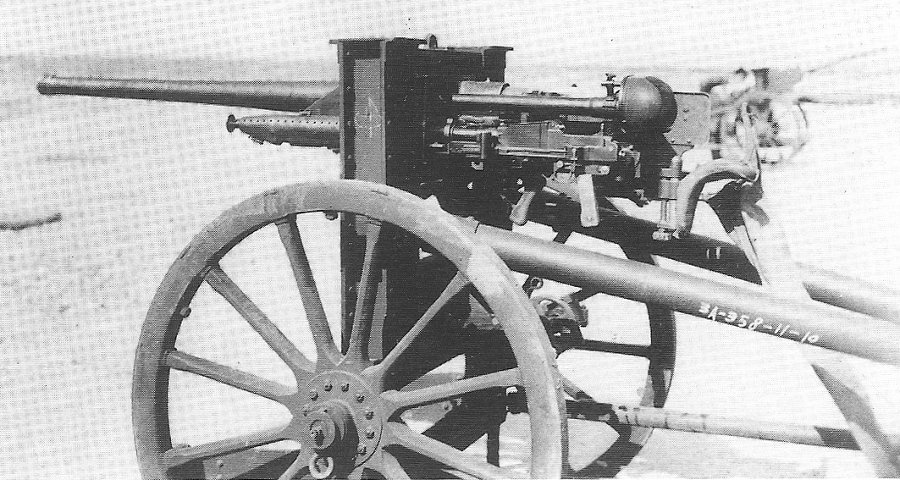
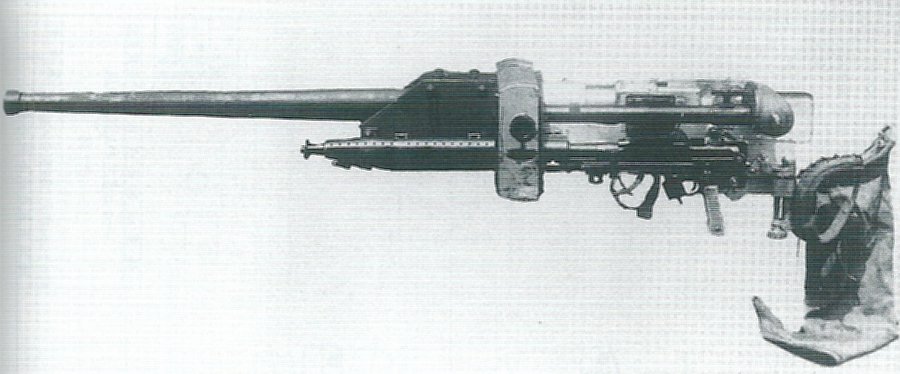
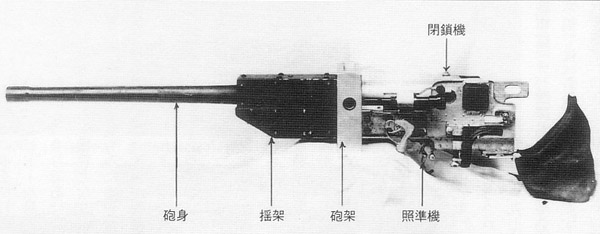
g) Type 92 13,2 mm Tank Machine Cannon

This MG was an IJA developed from the french Hotchkiss 13,2 mm AA-MG and should not be mixed up with the IJN Type 93 13,2 mm Machine Cannon which was an only slightly modification.
The Type 92 Machine Cannon received a shorter barrel to reduce recoil. A butt stock was added to fire it from the gunner´s shoulder. It fired the Typ 93 Machine Cannon ammunition from a 20 shot clip.
This weapon was used by the Type 92 Heavily armoured vehicle exclusively. It was mounted in a modified standard MG-mount in the oriel in the right. With this mount even aa-fire was possible but to do so the gunner had to lay on the floor looking upwards. This only allowed barrage firing.
no data found
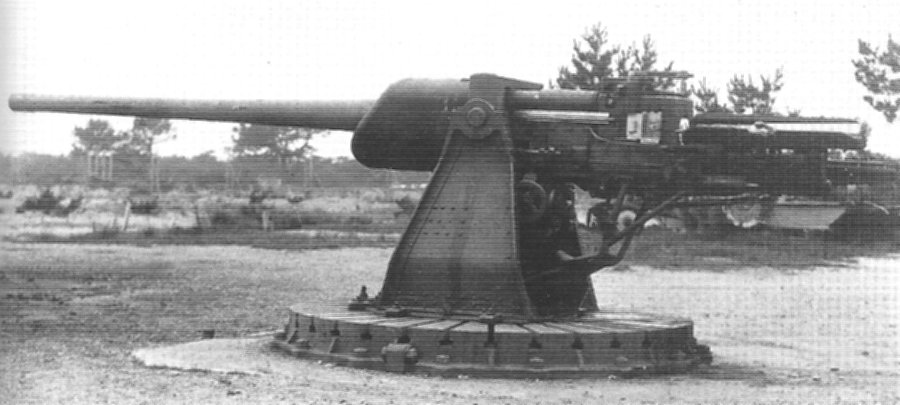
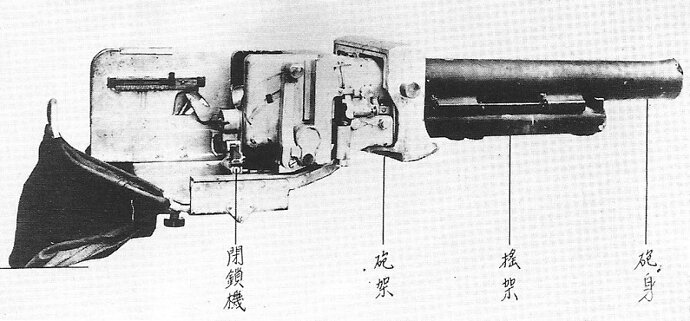
h) Type 96 25 mm Machine Cannon
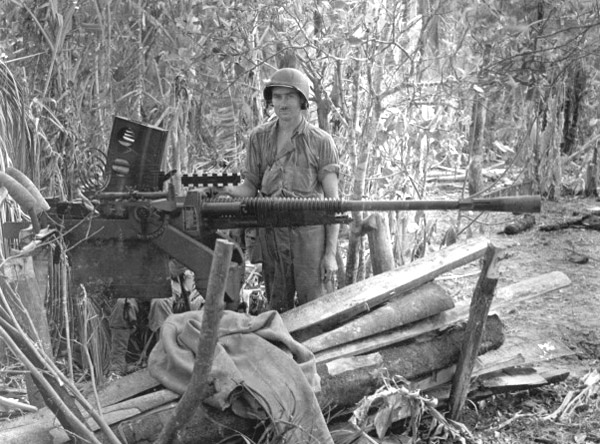

In 1944 IJN decided to develop a version of this aa-gun for the use in their new development of an amphibious tank model. It was planned to equip the turret with this gun. So several changes were made including a new muzzle brake, a shorter barrel and a smaller recoil mechanism. The gun was never adopted officially as the tank development was ceased in spring 1945.
no data found
Yours
tom! 




































 ]
]






