KURSK - the greatest tank battle of World War 2
The last major German offensive in the East
In the winter and spring of 1943, after their terrible defeat in Stalingrad, clearly outnumbered and losing the initiative in the eastern front, Hitler and the German High Command were asking themselves what to do next, in the summer of 1943.
The situation was bad not only on the war front.
While Russian tank production increased to unbelievable levels, the German obsession for complex new super weapons, like the advanced but then immature Panther and Tiger tanks, largely reduced German tank production.
General Guderian, the best German armor expert and commander, said:
As interesting as these designs were, the practical result was just a reduced production of the Panzer 4, our only efficient tank then, to a very modest level…
Shortly before the battle of Kursk Guderian added, about the Panther and its crews:
They are simply not ready yet for the front.
In early 1943 the Germans were about to destroy their own tank production rates by terminating Panzer 4 production in return for a production of just 25 new Tigers per month, but at a moment of reason Hitler gave control of tank production to Guderian who stopped this idea.
The German plan
The debate in the German High Command about what to do in the summer of 1943 was between two options, the realistic option and the enthusiast-optimist option:
The realistic option, supported by Guderian and Manstein, the best German field commanders, and by others, suggested to compensate for the large Russian numerical advantage by fully utilizing the superiority of the German commanders and soldiers in tactics, command, and fighting, by a strategy of dynamic mobile defense that would cause great losses to the Russians in a series of local clashes. The realistic goal was to stop and delay the Russians, as decisive victory was no longer achievable.
The enthusiast-optimistic option, proposed by General Zeitzler, chief of staff of the German army, suggested to concentrate almost all German tanks, and other forces, to a major decisive battle against a large portion of the Russian armor, in order to destroy them and by doing so hopefully regain the initiative. The most suitable place for such a battle, as Zeitzler proposed, was the Kursk salient, a wide region around the city of Kursk, about half way between Moscow and the black sea, where the Germans surrounded the Russians from three sides. It was obvious that the Russians will keep a large tank force there, and the plan was to encircle them in a classic Blitzkrieg style pincer movement of German tanks from North and South and destroy them. Zeitzler’s plan was code named Operation Citadel.
When Hitler discussed the two options with his Generals on May 4th, exactly two months before the German attack began, it became clear that each of the two options had a major problem.
The major problem with Zeitzler’s plan to attack the Kursk salient, was that aerial photos clearly revealed that the Russians were building dense and deep fortifications there in order to counter such an attack, and that many Russian tanks were moved deeper behind the front line. Instead of an open battlefield Blitzkrieg, it was going to be a direct charge on dense anti-tank defences. General von Mellenthin warned that such a direct attack will be a “Totenritt”, a ride to death, for the German tanks. In response to Guderian’s worries, Hitler himself admitted that whenever he think of this planned attack, his guts turn.
The major problem with Guderian’s option was that it lacked the charm, enthusiasm, and optimistic hope for a major change in the war that Zeitzler’s plan had. So the enthusiast Hitler decided in favor of Zeitzler’s plan, and calmed his worries of it by ordering to delay the attack for a while in order to incorporate more of the brand new advanced German tanks and tank destroyers in it. The date was set to July 4, 1943.
Once the order was given, the Germans prepared as best as they could. The entire region was photographed from above, the German commanders visited the front line to observe their intended routes, and the Germans concentrated all available forces in two armies, North and South of the Kursk salient, leaving minimal forces along the rest of the long Russian front.
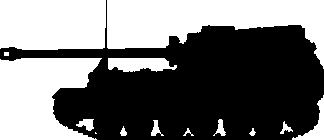
The German force included a total of 50 divisions, including 17 armor and mechanized divisions. These included the most powerful and best equipped German divisions, such as the Gross Deutschland (Great Germany) division and the Waffen-SS tank divisions Leibstandarte (Hitler’s bodyguards), Totenkopf (Death skull), and Das Reich (The Reich). The Germans concentrated all their new armor, the Tiger and Panther tanks, and the mighty new Elefant tank destroyers, which had a front armor thicker than a battleship’s armor. They also concentrated all available air units and artillery, and despite the problems of the German plan it was a formidable concentrated mobile armor force with great offensive potential.
The Russian preparations
Thanks to their “Lucy” spy network, which operated high ranking sources in Germany via Switzerland, the Russians didn’t just expect the German attack, they knew all about it. They received the full details of the German plan, and the Russian military intelligence was able to verify most details in the front to ensure that the information was real, not disinformation.
The Russians prepared eight defence lines one behind the other, and also positioned their entire strategic mobile reserve East of the Kursk salient, in case the Germans will penetrate thru all these defence lines, which indeed happened.
The Russian plan was simple. First, they will let the Germans attack as planned right into their series of very dense defence lines, and after the German armor will be crushed there, the Russian army will start its strategic attack North and South of the Kursk salient and push the Germans West along a wide part of the front.
The Russian defence was unprecedented in its density. A total of 1,300,000 Russian soldiers with 3600 tanks, 20,000 guns, including 6000 76mm anti-tank guns, and 2400 aircraft were concentrated in and around the Kursk salient. It was about a fifth of the Russian military personnel, over a third of the tanks and over 1/4 of the aircraft. They laid 3400 mines per each kilometer of the front, half of them anti-tank mines, and over 300,000 civilians dug thousands of kilometers of anti-tank trenches and other fortifications. The Russian lines were filled with numerous anti-tank guns organized in groups of up to 10, each group commanded by one officer and firing at the same target. The Russian camouflage was superb, the Germans said that until they were hit by them, they could identify neither the Russian mine fields nor their anti-tank gun positions. To avoid forcing the Germans to divert from their known plan, Russian air attacks were delayed until the German tanks already moved into the trap. The Russians were as ready as they could be.